Testing: The Art of Destruction. An integral part of Quality Assurance.
Productive QA:
Analytical QA: Compromises activities which ascertain its level of Quality. Software Testing comes under Analytical QA.
Software Testing:
1. Testing involves operation of a system or application under controlled conditions and evaluating the results.
2. Every Test consists of 3 steps :-
Planning : Inputs to be given, results to be obtained and the process to proceed is to planned.
Execution : preparing test environment, Completing the test, and determining test results.
Evaluation : compare the actual test outcome with what the correct outcome should have been.
‘Pareto principle’ - says that 80% of the errors are concentrated at 20% of the code only – forms a good criteria for testing.
Classifications in Testing:
Various methodologies of testing exist which can best be classified into 2 major categories:
Testing Methods:
Black Box Testing:
Comparison Testing
Graph Based Testing
Boundary Value Testing
Equivalence class Testing
Gray Box Testing:
Similar to Black box but the test cases, risk assessments, and test methods involved in gray box testing are developed based on the knowledge of the internal data and flow structures.
White Box Testing:
Mutation Testing
Basic Path Testing
Control Structure Testing
Testing Levels:
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Black Box Testing:
Also called ‘Functional Testing’ as it concentrates on testing of the functionality rather than the internal details of code.
Test cases are designed based on the task descriptions.
Equivalence Class Testing: Test inputs are classified into Equivalence classes such that one input check validates all the input values in that class.
Boundary Value Testing: Boundary values of the Equivalence classes are considered and tested as they generally fail in Equivalence class testing.
Comparison Testing: Test cases results are compared with the features/results of other products e.g. competitor product.
Graph based Testing: Cause and effect graphs are generated and cyclometric complexity considered in using the test cases.
White Box Testing:
Also called ‘Structural Testing / Glass Box Testing’ is used for testing the code keeping the system specs in mind.
Inner working is considered and thus Developers Test.
Mutation Testing: Number of mutants of the same program created with minor changes and none of their result should coincide with that of the result of the original program given same test case.
Basic Path Testing: Testing is done based on Flow graph notation, uses Cyclometric complexity & Graph matrices.
Control Structure Testing: The Flow of control execution path is considered for testing. It does also checks:-
Conditional Testing: Branch Testing, Domain Testing.
Data Flow Testing.
Loop testing: Simple, Nested, Conditional, and Unstructured Loops
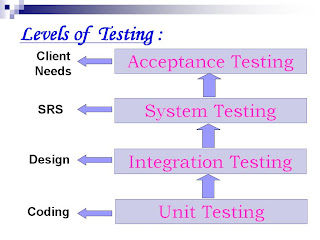
Unit Testing:
Unit Testing is primarily carried out by the developers themselves.
Deals functional correctness and the completeness of individual program units.
White box testing methods are employed.
Integration Testing:
Deals with testing when several program units are integrated.
Regression testing: Change of behavior due to modification or addition is called ‘Regression’. Used to bring changes from worst to least.
Incremental Integration Testing: Checks out for bugs which encounter when a module has been integrated to the existing.
Smoke Testing: It is the battery of test which checks the basic functionality of program. If fails then the program is not sent for further testing.
System Testing:
Deals with testing the whole program system for its intended purpose.
Recovery testing: System is forced to fail and is checked out how well the system recovers the failure.
Security Testing: Checks the capability of system to defend itself from hostile attack on programs and data.
Load & Stress Testing: The system is tested for max load and extreme stress points are figured out.
Performance Testing: Used to determine the processing speed.
Installation Testing: Installation & uninstallation is checked out in the target platform.
Acceptance Testing:
UAT ensures that the project satisfies the customer requirements.
Alpha Testing: It is the test done by the client at the developer’s site.
Beta Testing: This is the test done by the end-users at the client’s site.
Long Term Testing: Checks out for faults occurrence in a long term usage of the product.
Compatibility Testing: Testing to ensure compatibility of an application or Web site with different browsers,
For more software testing definitions, please go here



No comments:
Post a Comment